Mill Grinding Balls, Grinding Cylpebs and Grinding Rods

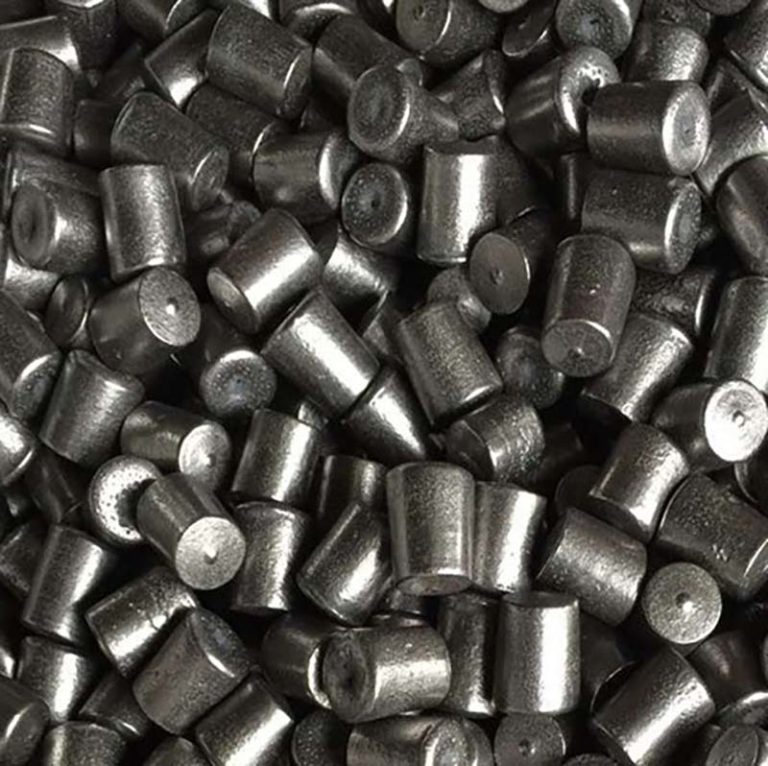
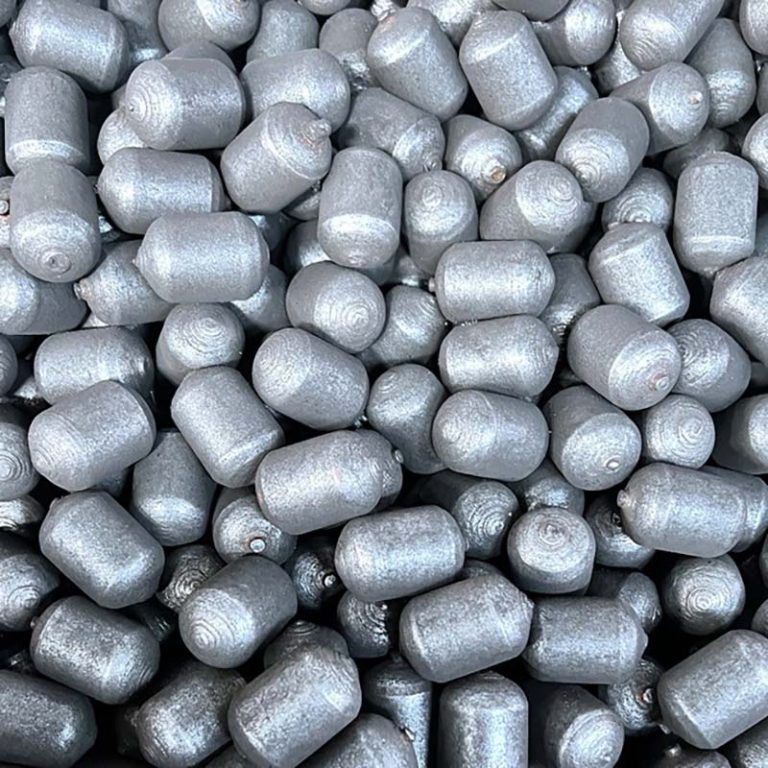
Medium Chrome Alloy Casting Steel Cylpebs ZQCr5
PRODUCT PARAMETERS
Diameters (mm): 8-55mm
Diameter tolerance: ±1
Length tolerance: ±2
Hardness(HRC): >47
Breakage rate: <1%
Impact value(J/cm²): >2
Dropping Test: ≥10000
MOQ: 20ft container (25 tons)
Description
Diameter tolerance and Length tolerance
| Diameter(mm) | 8×10 | 10×12 | 12×14 | 14×16 | 16×18 | 18×20 | 20×25 |
| 25×30 | 30×35 | 35×40 | 40×45 | 45×50 | 50×55 | 55×60 | |
| Diameter tolerance(mm) | +1,-1 | ||||||
| Length tolerance(mm) | +2,-2 | ||||||
Technical specification
| Material Gr. | Diameter(mm) | Hardness(HRC) | Breakage rate | Impact value(J/cm²) | Drop times(times) | Micro structure |
| ZQCr5 | 17-150 | >47 | <1% | >2 | ≥10000 | M+C |
Chemical composition
| Material Gr. | Chemical composition(%) | ||||||||
| C | Si | Mn | Cr | Mo | Cu | Ni | P | S | |
| ZQCr5 | 2.1-3.3 | 1.5max | 0.3-1.5 | 4.0-6.0 | 0-1.0 | 0-0.8 | - | ≤0.10 | ≤0.10 |

1. Composition
- Medium Chrome Alloy: Typically contains 5–10% chromium, balancing cost and performance. Carbon content ranges from 1.0–2.5%, with additions of manganese, silicon, and molybdenum to enhance toughness and moderate wear resistance.
- Casting Steel: Produced by pouring molten alloy into molds, followed by controlled heat treatment to refine microstructure.
- Cylpebs: Cylindrical grinding media (25–100 mm in size) with a truncated conical shape, optimizing surface contact in mills compared to spherical balls.
2. Properties
- Hardness: 50–60 HRC (lower than high chrome), due to fewer chromium carbides and a tempered martensitic/bainitic matrix.
- Wear Resistance: Moderate, relying on dispersed carbides (e.g., Cr₃C₂) and matrix hardness. Suitable for less abrasive environments.
- Impact Toughness: Higher than high chrome alloys due to reduced carbide volume and ductile microstructure.
3. Manufacturing Process
- Casting: Molten alloy is poured into molds to form near-net-shape cylpebs.
- Heat Treatment:
- Quenching: Air or oil cooling to form martensite/bainite.
- Tempering: Performed at higher temperatures (compared to high chrome) to enhance toughness and reduce brittleness.
- Finishing: Machined for dimensional precision and surface smoothness.
4. Applications
- Industries:
- Cement production (grinding clinker with moderate abrasiveness).
- Coal pulverization (lower abrasion, higher impact resistance required).
- Non-metallic mineral processing (e.g., limestone, gypsum).
- Advantages:
- Lower upfront cost than high chrome alloys.
- Better impact resistance in mixed abrasion-impact conditions.
5. Performance Comparison with High Chrome Alloys
| Chromium Content | 5–10% | 10–30% |
| Hardness | 50–60 HRC | 58–68 HRC |
| Wear Resistance | Moderate | Superior |
| Impact Toughness | Higher | Lower |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost |
| Lifespan | Shorter (1–2x vs. low chrome) | Longer (2–3x vs. low chrome) |
1. Definition and Composition
- Medium Chrome Alloy: Typically contains 5–10% chromium, balancing cost and performance. Carbon content ranges from 1.0–2.5%, with additions of manganese, silicon, and molybdenum to enhance toughness and moderate wear resistance.
- Casting Steel: Produced by pouring molten alloy into molds, followed by controlled heat treatment to refine microstructure.
- Cylpebs: Cylindrical grinding media (25–100 mm in size) with a truncated conical shape, optimizing surface contact in mills compared to spherical balls.
2. Properties
- Hardness: 50–60 HRC (lower than high chrome), due to fewer chromium carbides and a tempered martensitic/bainitic matrix.
- Wear Resistance: Moderate, relying on dispersed carbides (e.g., Cr₃C₂) and matrix hardness. Suitable for less abrasive environments.
- Impact Toughness: Higher than high chrome alloys due to reduced carbide volume and ductile microstructure.
3. Manufacturing Process
- Casting: Molten alloy is poured into molds to form near-net-shape cylpebs.
- Heat Treatment:
- Quenching: Air or oil cooling to form martensite/bainite.
- Tempering: Performed at higher temperatures (compared to high chrome) to enhance toughness and reduce brittleness.
- Finishing: Machined for dimensional precision and surface smoothness.
4. Applications
- Industries:
- Cement production (grinding clinker with moderate abrasiveness).
- Coal pulverization (lower abrasion, higher impact resistance required).
- Non-metallic mineral processing (e.g., limestone, gypsum).
- Advantages:
- Lower upfront cost than high chrome alloys.
- Better impact resistance in mixed abrasion-impact conditions.
5. Performance Comparison with High Chrome Alloys
| Chromium Content | 5–10% | 10–30% |
| Hardness | 50–60 HRC | 58–68 HRC |
| Wear Resistance | Moderate | Superior |
| Impact Toughness | Higher | Lower |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost |
| Lifespan | Shorter (1–2x vs. low chrome) | Longer (2–3x vs. low chrome) |
6. Standards and Quality Control
- Standards:
- ASTM A532 (Class I or II, depending on chromium and carbide content).
- ISO 9001 for quality assurance.
- Testing:
- Hardness testing (Rockwell C).
- Microstructure analysis (carbide distribution, matrix phases).
- Impact testing (Charpy V-notch) to validate toughness.





REQUEST A QUOTE
FAQs
Forged grinding balls are made by heating and shaping high-carbon or alloy steel under high pressure, resulting in superior hardness, impact resistance, and longevity. Cast grinding balls are produced by melting and pouring metal into molds, offering a cost-effective solution for less demanding grinding environments. Forged balls excel in high-impact mining operations, while cast balls are ideal for lower-impact scenarios like cement or coal grinding.
Choose forged balls for high-impact, large-scale mining (e.g., copper, gold) where durability and low wear rates are critical.
Choose cast balls for cost-sensitive applications with softer materials (e.g., limestone, coal) or smaller operations.
Make amazing 60-degree bevel cuts with our 8-1/4 in. SKIL Worm Drive Skilsaw model SPT78W-01. This Skilsaw is powered by our largest 15 amp Dual-Field™ high torque motor so you will make the last cut as precisely as you did the first cut. Exclusive 60-degree bevel. High torque Dual-Field™motor. Legendary SKIL durability.
Yes! We offer fully customizable solutions. Specify your required diameter (e.g., 20–150mm for balls), hardness (HRC 50–65), and material composition to match your mill’s operating conditions (e.g., ore hardness, rotation speed).
- Grinding Rods: Made from high-carbon steel or alloy steel, heat-treated for optimal wear resistance and toughness.
- Mine Liners: Constructed from high-manganese steel, chromium steel, or composite alloys to withstand abrasion and impact in mills.
We ship globally, with major clients in South America, Africa, Australia, North America, and Southeast Asia.
Standard Products: 15–25 days after order confirmation.
Customized Orders: 25–35 days, depending on specifications.
Shipping: Delivery times vary by destination
Grinding balls/rods: Packed in steel drums or bulk bags with anti-rust treatment.
Mine liners: Wooden crates or pallets with waterproof wrapping.
We enforce strict quality control:
100% surface defect checks before shipment.
Raw material inspection (spectral analysis).
Hardness and impact testing (Rockwell, Charpy tests).
We enforce strict quality control:
100% surface defect checks before shipment.
Raw material inspection (spectral analysis).
Hardness and impact testing (Rockwell, Charpy tests).